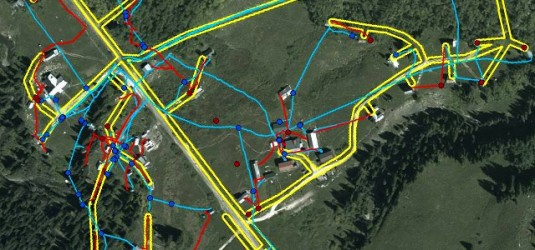
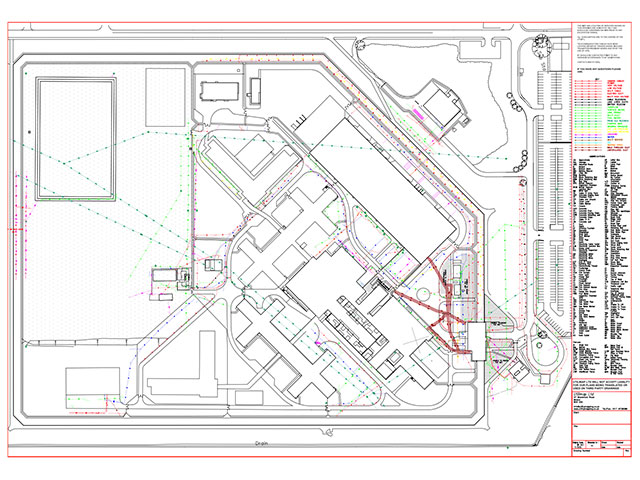
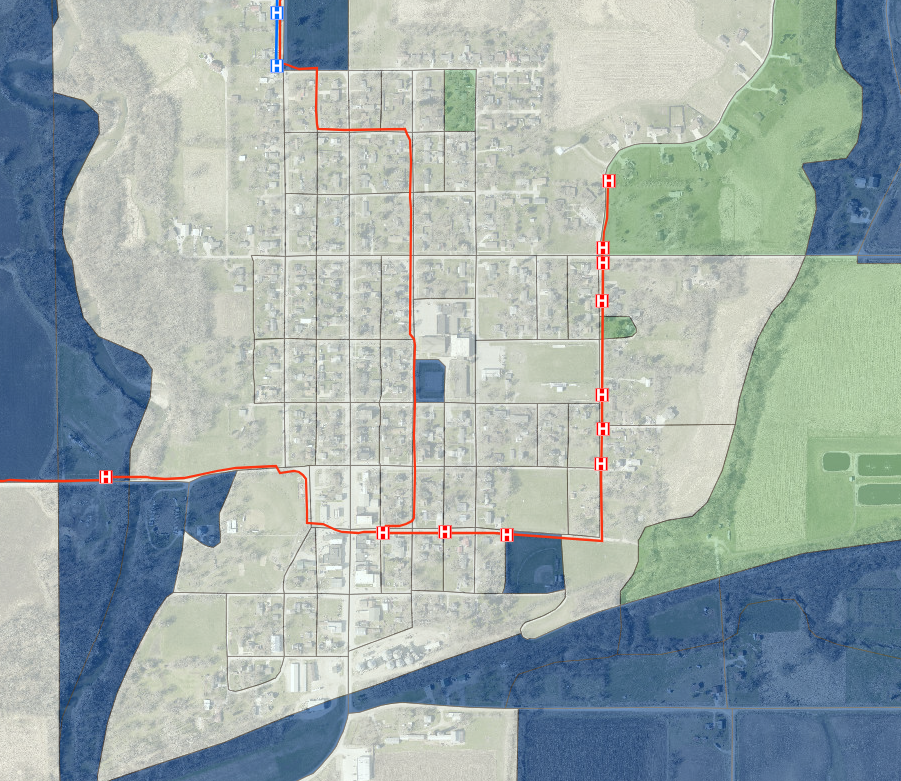
An underground utility map is an essential visual representation detailing the location of buried infrastructure such as water pipes, gas lines, electrical cables, and communication conduits. These crucial maps are vital for preventing accidental strikes during excavation, ensuring public safety, and facilitating efficient urban planning and development. Understanding how these intricate networks are mapped and managed is becoming increasingly important as cities expand and infrastructure ages. This comprehensive guide explores the significance of accurate underground utility mapping, its technological advancements, and its impact on construction, maintenance, and emergency response, providing critical insights for professionals and the public alike in 2026.
The Indispensable Role of Underground Utility Maps in Modern Infrastructure
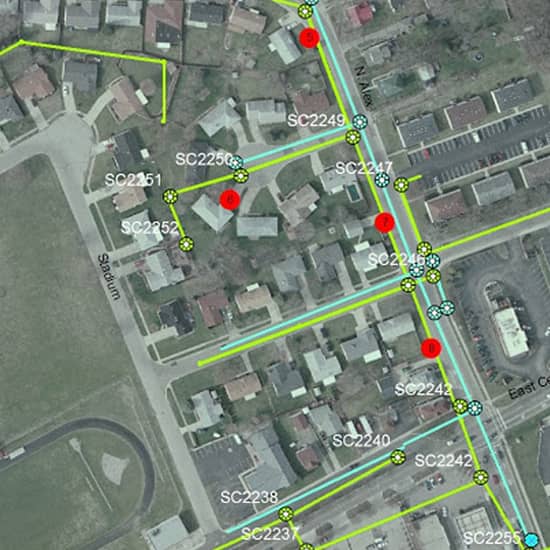
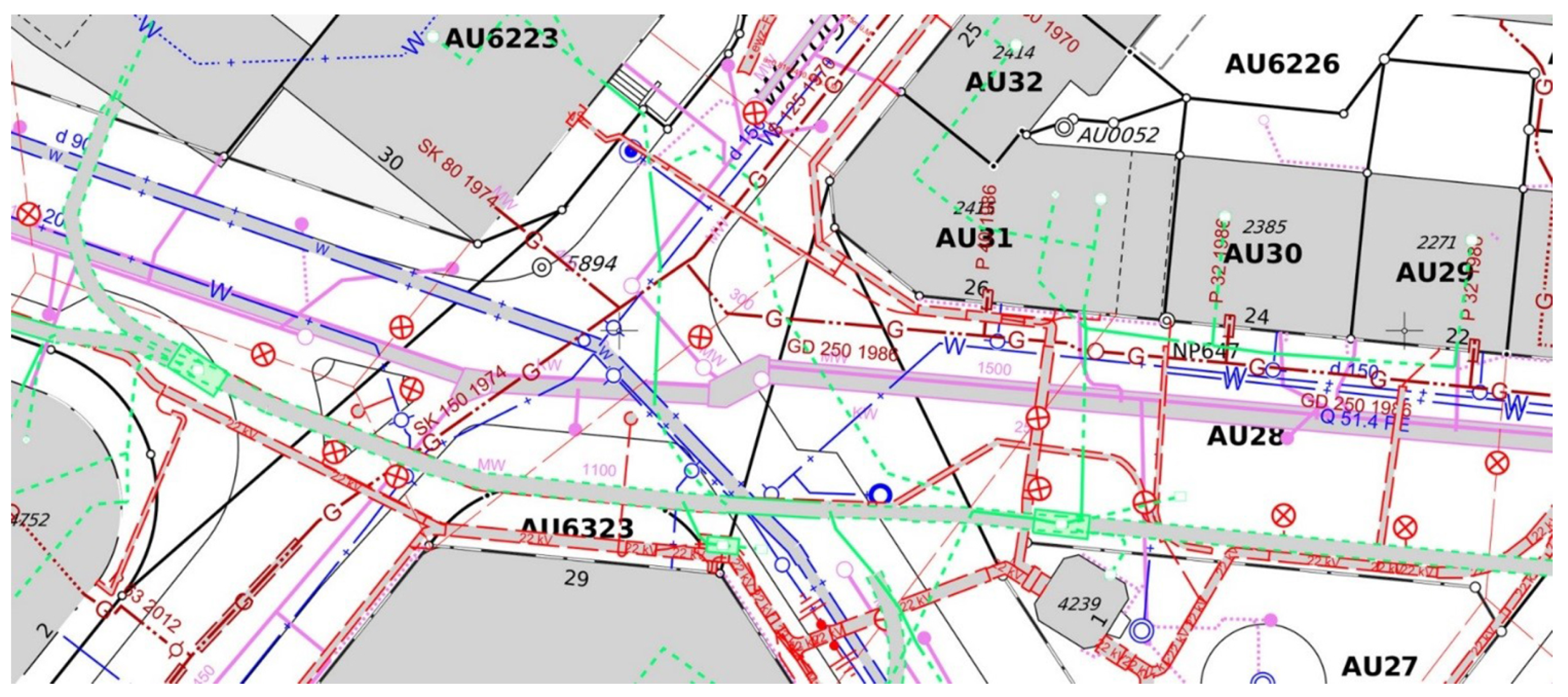
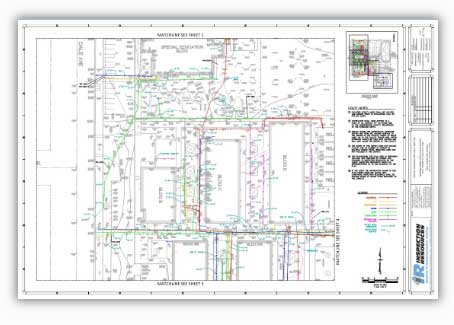
An underground utility map is a critical document. It visually details the precise location of subsurface infrastructure, including gas pipelines, water mains, electrical cables, fiber optics, and sewer lines. These maps are essential for anyone involved in excavation or development, from construction crews to city planners, ensuring safety, efficiency, and legal compliance. They act as a foundational guide for preventing accidental strikes on crucial utilities, protecting both workers and the integrity of essential services. Understanding and utilizing accurate underground utility maps is more vital than ever in 2026 as infrastructure projects continue to expand and evolve across the United States.
Why Underground Utility Maps Matter for Everyone
Underground utility maps are not just technical drawings; they are fundamental tools for public safety and economic stability in our communities. Imagine digging without knowing what lies beneath your feet. The risks are immense, from fatal accidents to widespread service disruptions. These maps proactively mitigate such dangers by providing clear, reliable information before any ground is broken for any underground utility map project.
Beyond safety, the economic impact of accurate underground utility maps is significant. Striking a utility can lead to exorbitant repair costs, project delays, legal disputes, and penalties. By preventing these incidents, good mapping practices save millions of dollars annually and keep crucial services flowing smoothly to homes and businesses across the nation, enhancing the reliability of every underground utility map.
How Are Underground Utility Maps Created and Maintained?
Traditional Methods for Underground Utility Map Creation
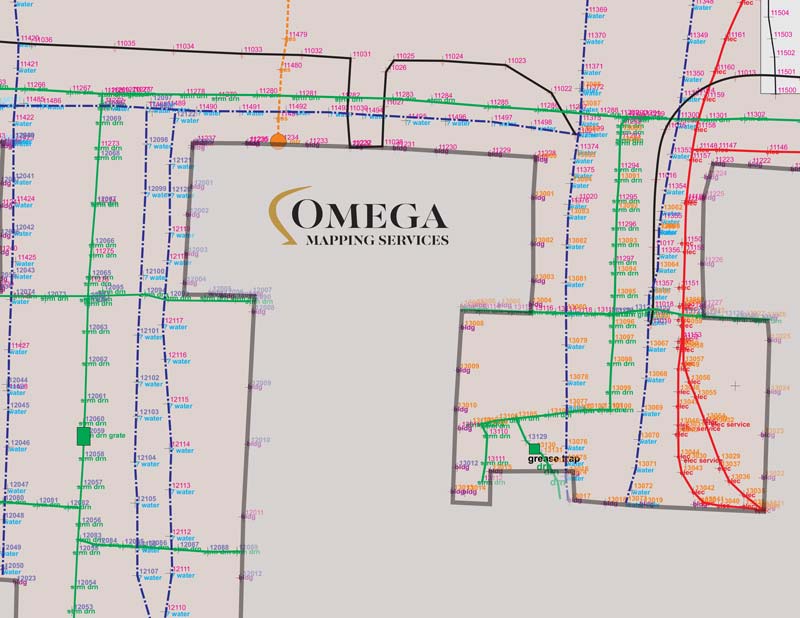
Historically, an underground utility map relied heavily on manual surveying techniques and a compilation of existing records. Engineers and surveyors would painstakingly gather information from as-built drawings, construction plans, and anecdotal evidence. This process often involved a mix of digging, probing, and cross-referencing paper documents. The resulting underground utility map was consequently prone to inaccuracies and gaps due to human error and outdated information.
Modern Technologies Revolutionizing Underground Utility Map Data
Today, the creation and maintenance of an underground utility map are transformed by advanced technologies. Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) and Electromagnetic Induction (EMI) are non-invasive methods. They detect subsurface features by sending signals into the ground and analyzing the reflections or induced currents. These technologies provide precise data on the depth and location of various utilities without excavation, significantly enhancing the accuracy of an underground utility map.
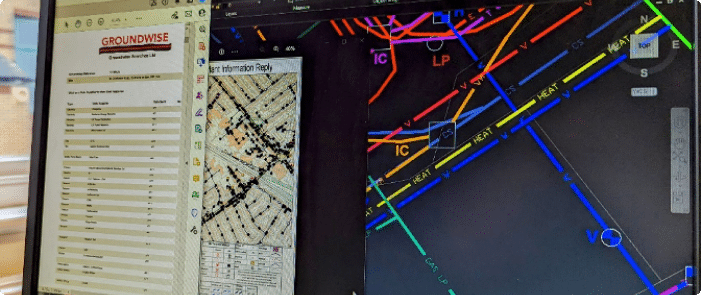
Geospatial Information Systems (GIS) play a crucial role by integrating this collected data into a comprehensive, layered digital map. GIS allows for the visualization, analysis, and management of vast amounts of spatial data. This makes the underground utility map dynamic and easily updateable. This digital approach ensures all stakeholders have access to the most current and detailed utility information, making project planning safer and more efficient.
Navigating the Complexities of Underground Utility Map Management
Despite technological advancements, managing an underground utility map presents ongoing challenges. The sheer volume of existing infrastructure, coupled with continuous development, means that maps can quickly become outdated if not regularly updated. Inaccurate data on an underground utility map can lead to significant project setbacks and dangerous situations. This emphasizes the need for meticulous data collection and verification for every underground utility map.
Legal and regulatory frameworks, such as "Call Before You Dig" programs (like 811 in the United States), are crucial in ensuring the use of underground utility maps. These regulations mandate that excavators contact a one-call center before digging. This prompts utility companies to mark their lines based on available underground utility map data. Adherence to these protocols is essential for protecting both infrastructure and lives across the nation.
What Others Are Asking? Underground Utility Map Edition
What is an underground utility map?
An underground utility map is a specialized drawing or digital representation. It shows the precise location, depth, and type of buried infrastructure. This includes essential services like water pipes, gas lines, electrical conduits, and telecommunication cables that run beneath the ground.
Why are underground utility maps important?
Underground utility maps are critical for safety and efficiency. They prevent accidental strikes on buried lines during excavation. Such strikes can cause severe injuries, service outages, property damage, and costly repairs, ensuring construction projects proceed smoothly and safely.
How do you locate underground utilities without a map?
Locating utilities without an underground utility map typically involves using specialized equipment. This includes Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) or electromagnetic pipe and cable locators. Professionals often employ these non-invasive technologies to detect and trace subsurface infrastructure before any digging commences.
Who is responsible for underground utility mapping?
Utility companies are generally responsible for mapping their own lines, often collaborating with local government agencies and private mapping firms. Property owners are responsible for private lines on their property. States enforce "Call Before You Dig" laws requiring utility notification, ensuring a comprehensive underground utility map.
How accurate are underground utility maps?
The accuracy of underground utility maps varies widely. It depends on their age, the methods used for their creation, and the frequency of updates. Modern techniques like SUE (Subsurface Utility Engineering) and GPR offer high precision, significantly improving reliability compared to older, hand-drawn records for any underground utility map.
FAQ About Underground Utility Map Systems
Who Uses an Underground Utility Map?
Construction companies, utility providers, city planners, emergency responders, and even homeowners planning landscaping projects rely on underground utility maps. They are essential for anyone whose work involves disturbing the ground safely.
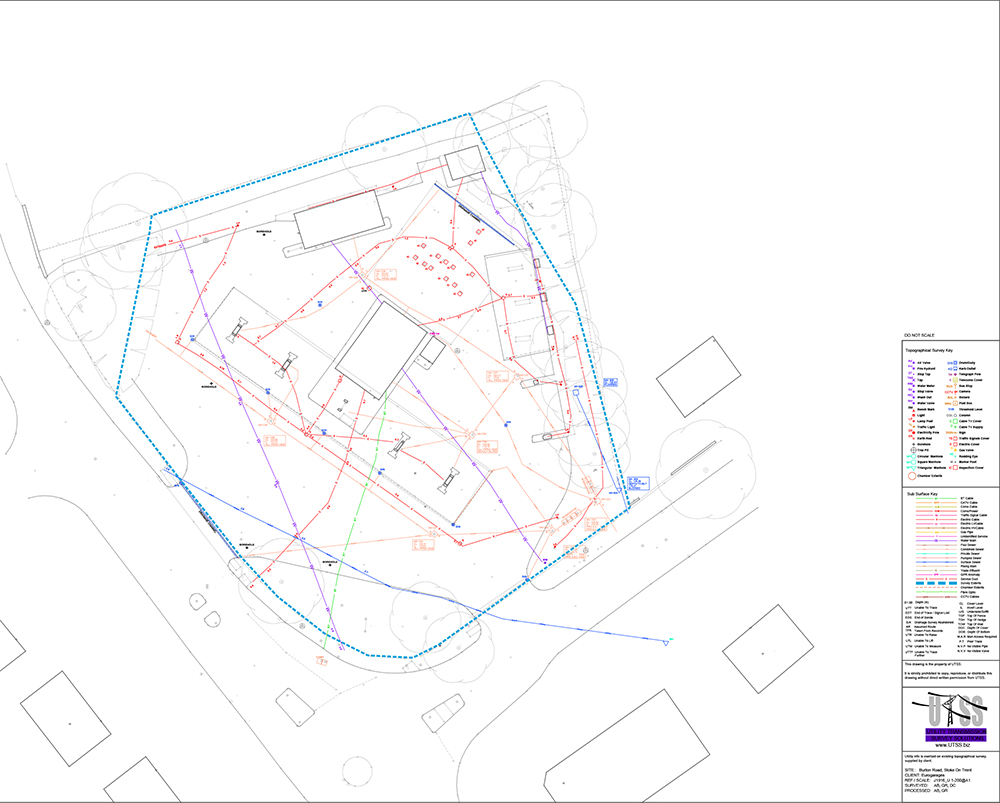
What Information Does an Underground Utility Map Contain?
These maps typically show the type of utility (e.g., gas, water, electric), its material, diameter, depth, and precise horizontal location. They also include relevant identifying markers and sometimes the owner of the utility provider for an underground utility map.
Why Do We Need Accurate Underground Utility Maps?
Accurate underground utility maps are vital for preventing dangerous accidents, costly service disruptions, and legal liabilities. They ensure public safety, protect critical infrastructure, and facilitate efficient urban development. An up-to-date underground utility map saves lives and resources.
How Can I Access an Underground Utility Map?
You can typically access utility information through your local 811 "Call Before You Dig" service. This notifies utility owners to mark their lines. For specific project planning, professionals might engage Subsurface Utility Engineering (SUE) firms to create or verify an underground utility map.
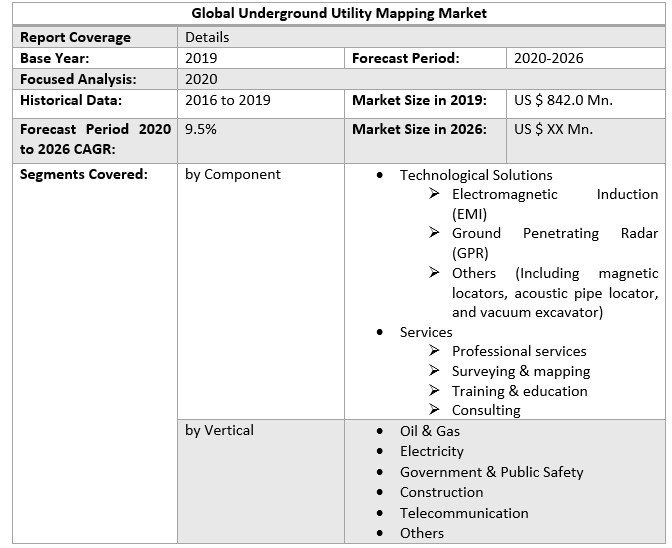
A Table of Underground Utility Map Technologies
| Technology | Description | Application for Underground Utility Map | Accuracy Level |
| Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) | Uses radar pulses to image the subsurface. | Detects non-metallic and metallic pipes, conduits, voids for the underground utility map. | High (within inches) |
| Electromagnetic Induction (EMI) | Detects metallic utilities by sensing their electromagnetic fields. | Locates metallic pipes, cables, and tracer wires for an underground utility map. | Medium to High (within feet) |
| Geospatial Information Systems (GIS) | Collects, stores, analyzes, and presents spatial data. | Integrates all utility data into a digital, interactive underground utility map. | Depends on input data quality |
| Subsurface Utility Engineering (SUE) | Comprehensive engineering practice for managing utility information. | Combines multiple technologies and data sources for precise mapping on an underground utility map. | Very High (highest standard) |
| Lidar (Aerial/Drone) | Uses pulsed laser to measure distances for 3D mapping. | Identifies surface features indicating utility presence. It can map above-ground assets for context for the underground utility map. | High for surface features |
The Future of Underground Utility Map Technology
The evolution of the underground utility map is moving towards greater digitalization and real-time updates. Imagine a world where every new utility installation or repair automatically updates a centralized digital underground utility map, accessible instantly to authorized personnel. This shift minimizes reliance on outdated paper records and fosters a more proactive approach to infrastructure management.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and predictive mapping are poised to further revolutionize the underground utility map. AI can analyze historical data, soil conditions, and past incident reports. It can predict potential utility locations or identify areas with a higher risk of undocumented lines. This foresight can make excavation projects safer and more efficient than ever before, marking a significant leap forward for every underground utility map in existence.
Summary of Key Points Underground Utility Map Importance
In conclusion, the underground utility map is far more than just a drawing. It is a critical safeguard for human lives, a protector of valuable infrastructure, and a driver of efficient urban development. From traditional methods to advanced GPR and GIS integration, the technology behind mapping our hidden networks continues to evolve. This promises greater accuracy and accessibility for every underground utility map. Adhering to "Call Before You Dig" protocols and investing in accurate, up-to-date underground utility map data remains paramount for anyone working beneath the surface. Embracing these tools not only prevents costly accidents but also builds safer, more resilient communities for the future.
Underground utility maps are crucial for safety during excavation, preventing costly damage, and supporting efficient infrastructure planning. They detail the exact location of essential services like water, gas, electricity, and telecommunications. Modern mapping techniques, including GPR and GIS, enhance accuracy and accessibility, making these maps indispensable for construction, maintenance, and emergency response. Adhering to 'Call Before You Dig' principles based on these maps is fundamental for protecting communities and assets.
Best Utility Locating Service Underground Utility Locator Home Page Utility Map See Sample 768x518 Benefits Of Underground Utility Mapping On The Mark Locators Map 550 Geographic Information Systems GIS City Of Amarillo COA Underground Utilities Map Thumbnail
Underground Utility Mapping Surveys Dom Latham 4 1 Private Underground Utility Locating Service Omega Mapping Services Utility Mapping Underground Utility Mapping What Is It Why It S Important 1st Img Underground Utility Mapping What Is It And Its Underground Utility Mapping And Locating Services In Washington Andover Map 2
Underground Utility Surveys Arc Surveys Underground Utility Surveys Utility Search Underground Utility Mapping Groundwise Sub Service Image Underground Utility Mapping UTSS Utility Survey Underground Utility Mapping Subsurface Mapping Aids Underground Utility Management 4M Analytics Utility Map
Best Utility Mapping Service Provider Util Locate Building Utility Mapping Services How Precision Underground Utilities Is Making Real Time High Accuracy Zoom In Underground Utility Blueprints Mapping Vantage Utility Connections Full Underground Mapping Survey
The Best Underground Utility Locating Service Helps Local HS Section4 Towards An Underground Utilities 3D Data Model For Land 11 01957 G006 Underground Utility Data Mapping Utilities Search Inc DOMN1611 Nokes Atlantic Utility Crossings 1 1000x674 768x497 Underground Utility Surveys Utility Survey Underground Utilities Ameys
Why Simplify Your Underground Utility Mapping GPRS Sitemap 3 Underground Map London The REAL London Underground Map Atkins To Deliver UK Wide Digital Map Of Underground Utilities New Iceberg High Res Trim 2 Underground Utility Blueprints Towards An Ecosystem Of Underground 37
Underground Map New York City Subway Route Map By Michael Calcagno TfL OgLoop V0512 Q8 72ppi 1024x1024 What Is Underground Utility Mapping Importance BenefitsUnderground Utility Mapping Market Scope Key Players 24b728c3 5d01 4212 A7be New Digital Map Of Underground Pipes And Cables On Track To Grow S300 NUAR GOV 1
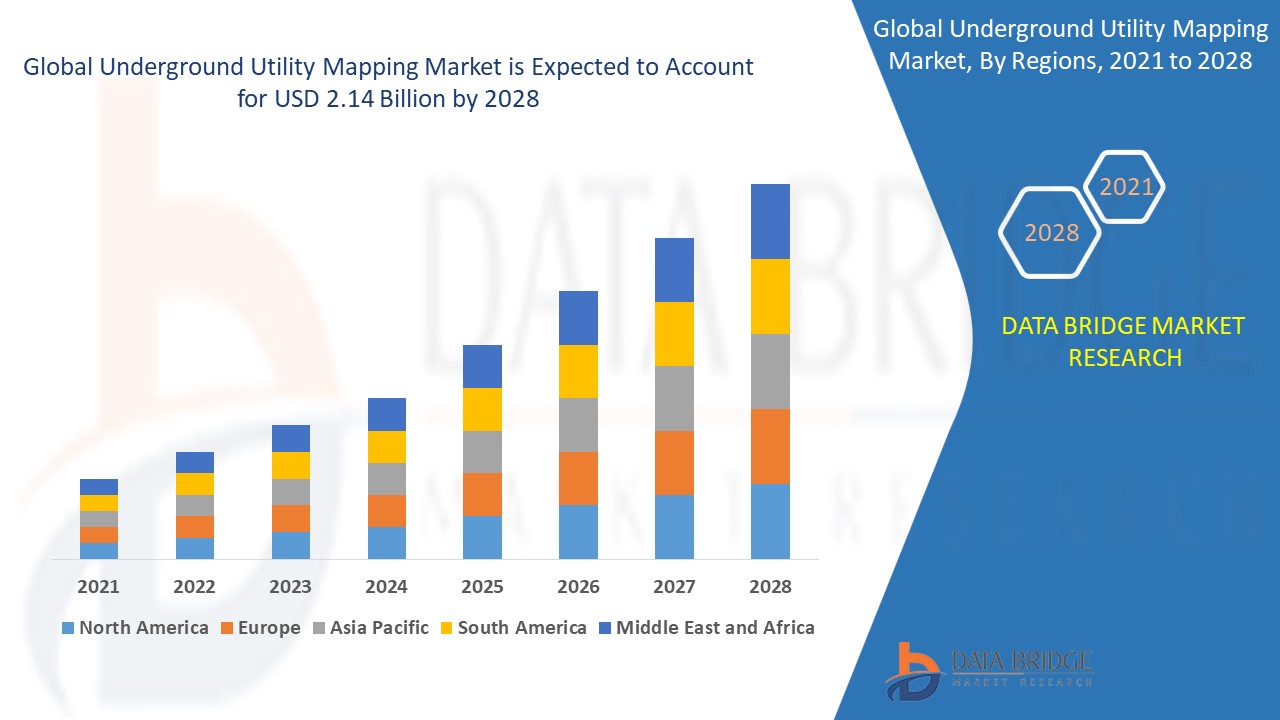
Valley Line West 2026 Route Map Railway News Railwa News Utility Mapping Services At Underground Detective Mapping Main 535x250 Accurate Underground Utility Mapping Services Genesis Land Survey PDF Accurate Underground Utility Mapping Services Genesis Land Survey 1 320 Global Underground Utility Mapping Market Industrial Analysis Global Underground Utility Mapping Market 2
Underground Utility Mapping Surveys Dom Latham 2 1 Utility Mapping Utility Surveys Drawings ADP Group Adp Landutility